What If Viagra Doesn’t Work? Penile Implants Explained By Our Experts
When oral Erectile Dysfunction drugs do not work
The introduction of sildenafil in 1998 initially reduced the number of implants placed two years after the number was doubled due to the growth in the number of patients requesting treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED).
In certain patients, sildenafil (Viagra) is partially or completely ineffective. Vascular pathology (35.3%) and diabetes (22.8%) constitute the causes for inefficacy of drugs like Viagra and other medications from its class (PDE5 inhibitors).
Other causes for PDE5 failure are:
- Peyronie’s disease, when associated with ED, is an occasional indication (13.5%) when the curvature is severe and stable. The intervention allows to correct at the same time the curvature (incision graft of albuginea or manual modelling on the implant) and the ED.
- The consequences of prolonged priapism are sometimes marked by a reluctant ED to any treatment, in connection with extensive fibrosis. This indication is rarer (2.2%) but may concern young people (sickle cell disease).
- Finally, the placement of a semi-rigid implant can allow the urinary apparatus of certain patients, neurological patients in particular.
- Treatment of ED post-prostatectomy (16.5%) requires an implant in case of ineffective rehabilitation to give patients spontaneous erections or under inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 5 (IPDE5), when injections or other treatments are considered to be ineffective or discarded as a short-term solution.
Treatment of erectile dysfunction is most often based on the intake of a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, or even on second-line treatment (intracavernous or intra-urethral prostaglandin E1, or even vacuum). In the event of failure of these treatments, the alternative is the installation of a penile implant.
Introduction to penile implants
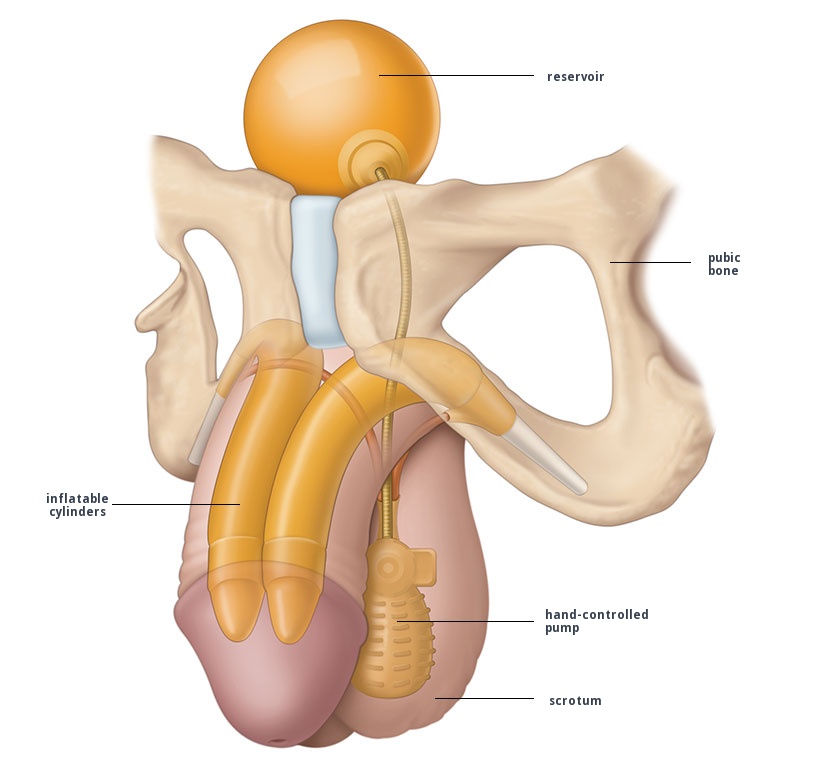 The implantation of a penile prosthesis is a solution to consider in the event of failure or contraindication to medical treatments. The patient must be motivated and informed of the risks, particularly infectious. A careful evaluation of the patient and his antecedents makes it possible to adapt the choice of the type of prosthesis. This treatment allows a high level of satisfaction to be obtained when the surgical technique is controlled and the patient is informed of the benefit of this treatment.
The implantation of a penile prosthesis is a solution to consider in the event of failure or contraindication to medical treatments. The patient must be motivated and informed of the risks, particularly infectious. A careful evaluation of the patient and his antecedents makes it possible to adapt the choice of the type of prosthesis. This treatment allows a high level of satisfaction to be obtained when the surgical technique is controlled and the patient is informed of the benefit of this treatment.
Inflatable penile implants have existed for 35 years and have enjoyed constant improvements. The technical characteristics of the current implants mean that the complications are now of medical origin in their great majority, and rarely of a mechanical order. Of all the implants used in medicine, the penile implant is the one with the highest satisfaction rate (over 90%) and the lowest revision rate (96% works at 5 years, more than 60% at 15 years). Two companies are manufacturing these implants, American Medical Systems and Coloplast (Mentor).
Informing the patient and his partner, if possible, is essential. This one concerns the advantages of the implant and its disadvantages (absence of erection of the glans). The definitive nature of the intervention must be underlined, the infectious risks and mechanical dysfunction also, as well as their consequences (resumption, change of prosthesis, even definitive ablation). The penile implant should not be offered to a patient with ED whose cause is reversible.
Intervention does not affect penile sensitivity, orgasm, or libido. It therefore does not restore them in the event of an attack associated with ED.
An important part of this interview is devoted to the evaluation of the patient’s motivation for the intervention and also makes it possible to exclude patients who are in fact looking at surgery to increase the volume of the penis or have inadequate results of the intervention.
Types of penile implants
There are two types of implants, semi-rigid implants and inflatable implants.
Semi-rigid implants offer a constant stiffness, the size of the penis being that obtained in flaccidity. The aesthetic and functional result is moderately satisfactory, but the advantage is that it is simple to understand and execute.
Inflatable implants are available in two-piece or three-piece models.
The three-piece models have two intracavernous cylinders, a scrotal pump and a retropubic reservoir. The cylinders are available in two widths, standard (AMS 700 CX, Coloplast Titan) or narrow (AMS CXR, Coloplast Titan Narrow Base). The narrow cylinders allow the implantation in case of fibrosated cavernous bodies and of cavernous dilation – mostly proximal – limited. The cylinders are available in widths up to 14 mm for narrow models, up to 18 mm for standard models.
The two-piece models consist of two cylinders and a scrotal pump. They offer the advantage of not necessarily requiring preperitoneal for the placement of the reservoir, the latter being integrated either to each of the two cylinders or to the scrotal pump. On the other hand, they do not make it possible to obtain complete flaccidity, giving a slightly less good aesthetic result than a three-piece implant in the flaccid state. Moreover, the erection obtained is less rigid than that obtained with a three-piece implant, the reservoir being of restricted capacity.
The latest technical advances lie in the appearance of implants whose expansion in filling takes place in diameter and in length, reproducing more faithfully the natural cavernous erection. The other notable innovation is the addition of an antibiotic-impregnated coating (InhibiZone® AMS® coating) or a hydrophilic coating to impregnate antibiotics in the prosthesis (Resist® Mentor®). The dimensions of the scrotal pumps have been reduced with the appearance of the latest models of the two manufacturers.
Penile prosthesis vs. Erectile Dysfunction drugs
The essential indication for choosing penile implants over oral drugs is ED resistant to first- and second-line treatments, either per-os, intracavernous, intra-urethral and vacuum treatments or having a contraindication to the use of these treatments. The patient’s refusal of these treatments as a definitive solution because of their cost, poor tolerance, incomplete efficacy is another classic indication of penile implants.
| Viagra and other PDE5 drugs | Penile implants | |
| Longevity | Taken as needed; effective during 4 hours | 5 years on average |
| Efficacy | 82% | 97% |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Invasive (penile surgery) |
| Complications | Side effects:
|
Infectious complications are the most severe. They concern 1.7 to 6.6% of patients according to the series of teams trained. Their rate decreases with the experience of the surgeon and his team. The infection may be immediate postoperative, involving high virulence, or at a distance (several weeks, or even several months postoperatively), involving low virulence germs. The latter do not appear to be favored by a poor diabetic equilibrium. Treatment of these infections requires prolonged antibiotic therapy and implant removal and replacement at the same time. Mechanical complications may include leakage of cylinders or tubing, erosion or aneurysm of a cylinder, or malfunction of the pump. The life expectancy of current implants exceeds 5 years at 85%. Other complications such as material migration, difficulties handling too deep a pump, erosion of corpus cavernosum, or auto-inflation of the implant usually require surgical recovery. |
| Cost | Circumstantial posology and related costs (generic Viagra cost ca. $0.77 – information by My Canadian Pharmacy Rx) | Single payment upwards of $18,000 and maintenance costs |
Approximate penile implants cost
The cost of penile implants is built up by the cost of the implant itself, which is graded by type and manufacture, surgeon’s fee; surgery room rent; post-op recovery facilities and costs. The risk of complications impose additional costs associated with their reversal.
Penile implants: before and after
 Penile implant, despite its ultimate treatment status, offers the best satisfaction rate of all ED treatments, being the most durable of them. This rate reaches 90% against 51% with sildenafil and 40% with intracavernous injections. Complications are divided into infectious, mechanical, or other complications.
Penile implant, despite its ultimate treatment status, offers the best satisfaction rate of all ED treatments, being the most durable of them. This rate reaches 90% against 51% with sildenafil and 40% with intracavernous injections. Complications are divided into infectious, mechanical, or other complications.
Inflatable penile implants are a reliable and satisfactory treatment for erectile dysfunction resistant to oral and intracavernous treatments. This treatment is for motivated and informed patients. Their implantation is associated with a low rate of complications.
The patient’s demand in terms of frequency of use and cosmetic result must be taken into account, his dexterity also (current and future in case of degenerative pathology), to allow the manipulation of the pump. Adequate understanding of the patient is also necessary in order to avoid certain complications due to incorrect use (implant permanently inflated for example). A history of pelvic surgery may cause a two-piece inflatable implant to be chosen in order to spare a second approach to the preperitoneal space in order to place the reservoir (enterocystoplasty, renal transplantation) in it. The implantation indication for urinary apparatus only concerns semi-rigid prostheses. Semi-rigid implants can also be offered to older or less skilled patients in the treatment of ED.