Sildenafil vs Tadalafil: The True Difference Between ED Blockbusters
Sildenafil: What Is It like?
Sildenafil is rightfully considered to be a pioneer among PDE5 inhibitors. It opened a new era in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, the era of effective peroral therapy. Sildenafil is a selective inhibitor of PDE5 which splits cyclic guanosine monophosphoric acid. When metabolism of nitrogen-oxide gets activated during sexual stimulation, inhibition of PDE5 prevents from destruction of cyclic guanosine monophosphoric acid which is the final and most active component causing the development of erection. Sildenafil meets all modern requirements for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. This substance is a highly effective and reliable oral agent, easy to use with few side-effects. However, it was noted that systemic adverse effects, although transitory, still have a significant impact on the patient’s well-being, especially when sildenafil is taken in large doses.
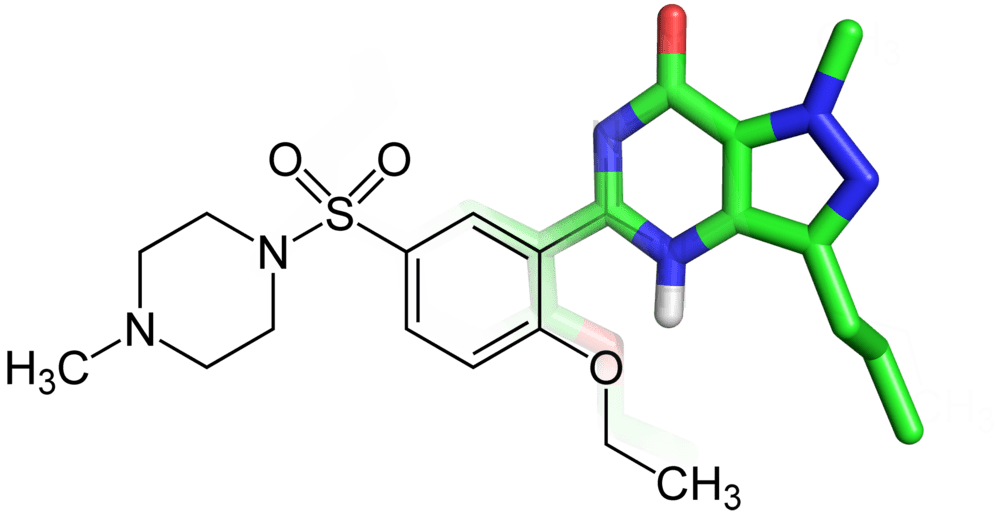
An essential contraindication to sildenafil use is application of drugs containing nitrates, which is very important, given that a man generally has erectile dysfunction accompanied by diseases of cardiovascular system. Clinical efficacy of sildenafil has been evaluated in numerous studies conducted around the world. The data obtained in 11 double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that included nearly 3000 patients with erectile dysfunction were combined. Twelve weeks after initial administration of the drug, 76% of men receiving sildenafil and 22% receiving placebo noted improvement in erection, with 66% of successful intercourse attempts and 26% in the first and second group, respectively. The effectiveness of various doses of sildenafil was 65% for 25 mg, 74% for 50 mg, and 82% for 100 mg. The agent is effective in patients with both organic and psychogenic erectile dysfunction. High efficacy of sildenafil is noted in different age groups. Thus, among patients aged under or above 65 years, the effectiveness of sildenafil was 77.6% and 69.2% accordingly.
The effectiveness of sildenafil is 66-90 per cent in cases of organic ED with good drug tolerability. Sildenafil efficiency in patients with diabetes varies between 59-61 per cent, with hypertension – 65-70per cent, with depression – 59-76 per cent, and with spinal cord injury -around 65 per cent. High efficacy of the drug, both in psychogenic and organic forms of erectile dysfunction, good tolerability and absence of pronounced side effects, compatibility with many drugs of different pharmacological groups allowed scientists to consider sildenafil to be the most suitable pharmacological agent for sexual adaptation of patients.
The dose of the drug is selected by titration starting with 50 mg with subsequent dose alteration (either decrease to 25 mg, or increase to 100 mg), depending on the effect and tolerability. Sildenafil is taken 1 time per day, 1 hour before expected sexual activity. The effect of the drug begins 40-60 minutes after administration and is preserved for 3-5 hours. The drug is well tolerated.
Generally, side-effects occur after the intake of 100 mg of sildenafil, but they are transient and are characterized by mild or moderate severity levels: headache (7%), redness of face and neck (7%), indigestion (2%), nasal congestion (1,5%) , vision impairment (1,1%). Very rarely, side-effects of sildenafil are the cause of discontinuation of treatment. The only contraindication to the use of sildenafil is nitrate therapy due to the risk of hypotension development. However, despite the high effectiveness of sildenafil (up to 85%), there are patients (15-42%) for whom the therapy with sildenafil is insufficiently effective or completely ineffective.
In recent years, the increasing interest has attracted the possibility of using sildenafil for various diseases accompanying erectile dysfunction. The effect of sildenafil for severe urinary disorders in patients with erectile dysfunction was evaluated. During the period of the 1st and 3rd months from the start of treatment, there was a significant decrease in the severity of lower urinary tract symptoms accompanied by improvement in erectile function.
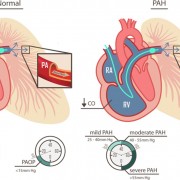
The use of sildenafil leads to improvement in the condition of patients suffering from primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Several experimental studies performed on animals showed a decrease in pressure in the pulmonary trunk due to sildenafil application. This fact became a prerequisite for studying the possibilities of using sildenafil in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. The effects of peroral intake of sildenafil were studied in patients with severe primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Medical experts noted a significant reduction in resistance of lung vessels and moderate increase in the cardiac index.
The possibility of using PDE5 inhibitors in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension of different origin was confirmed by a number of other studies. Researchers demonstrated a decrease in the size of the zone of myocardial infarction in a rabbit as a result of intravenous injection of sildenafil. Medical experts exposed that this effect was eliminated by the introduction of 5-hydroxydecanoate, an inhibitor of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels, which enabled them to associate the beneficial effects of sildenafil due to the action on these channels. While studying patients with heart failure, sildenafil had a moderate antiplatelet impact.
Do you want to learn more about Sildenafil Citrate and PDE5 inhibitors? We advise you to read these matreials:
What about Tadalafil?
Tadalafil was the next remedy- representative of PDE5 inhibitors on the market after sildenafil (Cialis). This drug was approved for use in Europe in February 2003. Tadalafil has all the advantages of PDE5 inhibitors, and it also has a number of unique properties. One of the main advantages of tadalafil is long-term elimination half-life (17.5 hours) and, accordingly, a prolonged effect of the drug. It is discovered that the improvement of the ability of men with ED to have sex is maintained for 36 hours after taking 20 mg of tadalafil. The effect of tadalafil does not depend on food intake that allows patients, especially young adults, to avoid planning sexual activity.
 To undoubted advantages of tadalafil in addition to its prolonged action and independence of meals allowing the patient to lead a habitual way of life without changing his habits and preferences, one can attribute convenience of use, which consists in the absence of necessity of dose titration. According to the results medical observations in the urology, tadalafil promoted spontaneity of sexual activity and improved sexual self-reliability, since patients thought less about the time allocated to them by the drug for sexual activity. The drug should be taken no oftener than once a day (20 mg) and, as opposed to sildenafil – fatty food and alcohol do not affect its pharmacokinetics. Tadalafil, as well as other inhibitors of PDE type 5, must not be combined with nitrates and nitrates-based medications.
To undoubted advantages of tadalafil in addition to its prolonged action and independence of meals allowing the patient to lead a habitual way of life without changing his habits and preferences, one can attribute convenience of use, which consists in the absence of necessity of dose titration. According to the results medical observations in the urology, tadalafil promoted spontaneity of sexual activity and improved sexual self-reliability, since patients thought less about the time allocated to them by the drug for sexual activity. The drug should be taken no oftener than once a day (20 mg) and, as opposed to sildenafil – fatty food and alcohol do not affect its pharmacokinetics. Tadalafil, as well as other inhibitors of PDE type 5, must not be combined with nitrates and nitrates-based medications.
The effectiveness of tadalafil is very high. In an integrated analysis of eleven randomized, placebo-controlled trials involving a total of 2100 ED patients, the success rate of sexual intercourse after taking tadalafil in the doses of 10 and 20 mg was 61% and 72% respectively, while in the placebo group this indicator was 34% (p <0.001). Improvement of the quality of erection as a result of taking 10 and 20 mg was observed – 71% and 84% of patients, respectively. The effectiveness of tadalafil in severe groups of patients is also high, reaching 64% of patients with diabetes, and 41% of those who underwent radical prostatectomy. The main side-effects of tadalafil were headache (12 -15%), dyspepsia (7-8%) and back pain (5-6%). The absence of influence on PDE6 by tadalafil, i.e. the absence of a side effect in the form of a change in color perception, characteristic of sildenafil, gives an additional advantage to tadalafil. Tadalafil was stopped due to side effects of 1,6% of patients who received it in the dose of 10 mg and 3,2% of patients in the dose of 20 mg.
Comparative Characteristics of Sildenafil and Tadalafil
Today, for clinical use, these both drugs from the group of PDE5 inhibitors have been approved:
- sildenafil (sildenafil citrate, Viagra, Pfizer Inc);
- tadalafil (Cialis, Eli Lilly ICOS LLC).
The mechanism of action of these two drugs is associated with competitive and reversible inhibition of PDE5 activity – the isoform of the phosphodiesterase enzyme that dominates cavernous tissue. The intracellular concentration of cyclic guanosine monophosphoric acid (the main molecule determining the tone of smooth muscle cells of cavernous tissue and penile vessels) is determined by the ratio between its synthesis with enzyme guanylate cyclase and the breakdown resulting from the action of PDE5. Inhibition of the latter leads to a significant increase in the content of cyclic guanosine monophosphoric acid in smooth muscle cells, which facilitates their relaxation and promotes the appearance of erection. It is important to note that the intake of PDE5 inhibitors does not cause erection, it requires sexual stimulation. Thus, both drugs are highly effective and safe remedies for treating erectile dysfunction with the same indications and contraindications to application.
At the same time, they have certain differences in efficacy and tolerability, which can vary quite individually in different patients. In the absence of clear medical criteria for drug selection, it is difficult to assess the influence of a factor on the preferences of a particular patient. The first results of comparative studies of various PDE5 inhibitors with an assessment of patients’ preferences are of high interest.
In 2003 the medical trial involved 91 patients with ED who took sildenafil on a regular basis and at least 4 times took tadalafil or vardenafil. The effectiveness of all three drugs was comparable; 19 patients preferred to switch to new medications (tadalafil or vardenafil), mainly because of better tolerability. In another study, conducted in 2003 involving 150 patients with ED where 24 (15%) were previously untreated and 126 (85%) were taking sildenafil. All patients were recommended a sequential intake of at least 6 tablets of each inhibitor of PDE5 (sildenafil, tadalafil or vardenafil). At the end of the study, 13% of patients preferred vasodilator therapy, vardenafil – 30%, tadalafil – 45% (in the overwhelming majority of cases because of its long-term effect).
In terms of the effect on endothelial function, sildenafil is the most well-studied drug, which is associated with its longer availability for clinical use. The use of sildenafil in doses of 25 to 100 mg was accompanied by improvement in systemic endothelial function in patients with heart failure, diabetes, coronary heart disease and addiction to smoking.
Given the same mechanism of action, similar results can be expected with other PDE5 inhibitors. This is confirmed by lots of researchers who showed that taking tadalafil once every two days for 4 weeks leads to improvement in the endothelial function of the brachial artery. Improvement of endothelial function in these individuals preserved even two weeks after discontinuation of the drug.
In conclusion of this section, it should be noted that the existence of two highly selective and effective PDE5 inhibitors – sildenafil and tadalafil used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, is an outstanding result of many years of research and clinical trials. Although these both drugs are comparable in their ability to inhibit PDE5, the differences in strength of action, interaction with food and alcohol, half-lives and other characteristics make certain that drugs are more suitable in certain clinical situations.
More Sildenafil and Tadalafil drug comparisons: