Attacking all the male age groups. Prostatitis.
Among all the diseases of male genital organs, inflammations should be considered separately, as they fall into the category of the most widely spread male health problems. Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate, a pathology that develops only in men. Until recently prostatitis was classified as a disease of the older patient group (50+ years old), but with the development of diagnostics methods the disease is now observed in younger patients (20+ years old).
Inflammation of the prostate is most often a result of another pathology. It may be a chronic disease of the genitourinary system, injury and so on. Importantly, even at a young age prostatitis can be combined with inflammation of the urethra or vesiculitis. As for the elderly suffering from the disease, hyperplasia of the body is oftentimes diagnosed at the same time. Treating inflammation of the prostate is very important, as prostatitis, particularly its acute form, significantly reduces the overall quality of life, being a widespread reason for a decline in potency.
Classification of prostatitis
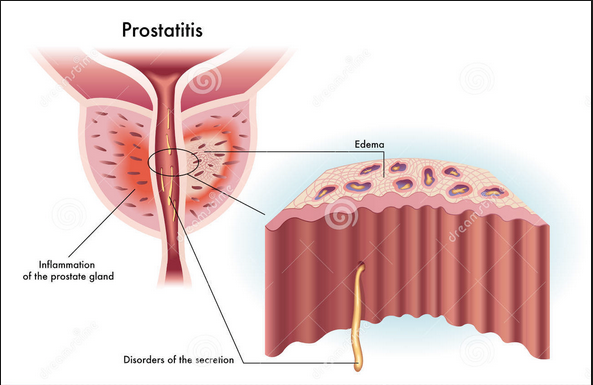
The disease can be diagnosed in acute, chronic bacterial and chronic non-bacterial form. The third type, in turn, is divided into the prostate both with the signs of inflammation, and without them.
Prostatitis can develop into a chronic asymptomatic form; and depending on the type of disease, symptoms and causes can be quite different. The most dangerous type is acute prostatitis form and it almost always requires emergency care.
As for chronic bacterial disease, it is characterized by sharp pain, painful urination, changes in the composition of body fluids (secretions of the prostate), and a number of less obvious reactions. This form is the most diagnosed one in the early age; and according to the statistics, the disease occurs in about 5-10% of the total male population. Chronic bacterial prostatitis significantly impairs life quality, that’s why the treatment is largely initiated by the patients themselves.
Causation of disease
Inflammation of the prostate, regardless of patient age group, has several key reasons. The acute form occurs because of a mass pathogenic microorganisms penetration into the body. This may be E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella and others. Under normal conditions they are permanent inhabitants of the skin and mucous membranes, but they enters the prostate, acute inflammatory reactions may follow. The causes of chronic bacterial diseases are more varied, although they can be divided into 2 large categories.
The first category includes common factors that can trigger inflammation: chronic infection, trauma or surgery, reduced resistance to infectious agents, physical inactivity, alcoholism, smoking, hypothermia and a few more. Interestingly, in people aged 20-50 years, microbes can get into the prostate in several ways. The first option is through the urinary tract (urethra) during a sexual intercourse, the second one – through the lymph and blood vessels.
The second category implies prostatitis as a result of destruction of other organs. Thus, bacteria can occur during tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis and even pustular skin lesions. There is a link between inflammation of the rectal mucosa and prostatitis. Non-bacterial form of the disease occurs several times faster than others. In this case the main etiological factors are: lack of exercise, blood stasis or gland secretion, hypothermia, poor nutrition, smoking, frequent alcohol consumption and failure of bladder emptying. In addition, the cause may be interrupted or too prolonged sexual intercourse, stress and sexual abstinence.
Prostatitis by Dr. Neil Baum, watch the following video:
Clinical symptoms of acute prostatitis
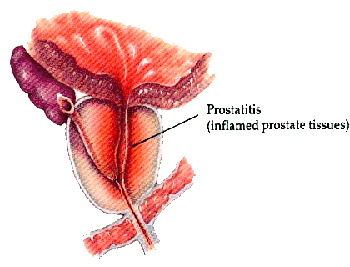
In acute exacerbation of chronic prostatitis the following common symptoms appear first: fever, weakness, chills. Another characteristic feature is pain. A person may feel pain in the perineum, lower abdomen, or just above the pubis. Pain may radiate. Of great importance is the fact that the pain gets worse after a bowel movement or during sex. Moreover, male patients may experience a burning sensation in the perineum.
In most male patients there is a violation of potency and ejaculation. Urine excretion becomes slower.
Acute prostatitis is dangerous because it can lead to the formation of abscess cancer. In this case, patient’s condition becomes severe. Defecation and urination are largely hampered.
Symptoms of chronic inflammation
Any 20+ years old male may suffer from chronic prostatitis. If the acute form lasts for approximately 1-2 months, then the periods of exacerbation and remission are be prolonged. The main features are: a burning sensation in the urethra, pain in the lumbar region/perineum/testicles and impaired urination. Erectile dysfunction is a rarer a symptom: it is manifested in a decrease in erection and pain during ejaculation.
The secretion of the prostate can flow when emptying the bowel and the changes in the nature of the seminal fluid are observed, as it becomes thinner and more turbid. This may decrease the number and mobility of the germ cells. Males with chronic inflammation of the prostate are often diagnosed persistent vegetative state, which manifests itself in fatigue, irritability and weakness. All of the above symptoms are pronounced only in the period of exacerbation, while clinical manifestations in remission are very rare.
More about Chronic Inflammation on Video:
Disease diagnosis
Diagnostics involves, first of all, the collection of medical history. The most valuable diagnostic criterion are the complaints of the patient and the results of laboratory and instrumental investigations. Blood and urine tests would be required to study the presence of seeding bacteria. And if its presence is confirmed, it indicates the nature of the bacterial prostatitis; if not, aseptic prostatitis is diagnosed.
Physician should rule out other diseases with similar symptoms. In the first place, a disease of sexually transmitted type. This is where determining the frequency of urination and the volume of biological fluid are crucial. To detect changes of the prostate, ultrasound of the body is conducted, plus it is also recommended to undergo pelvic organs ultrasound. A more accurate diagnosis can be conducted with an urography test.
Therapeutic activities
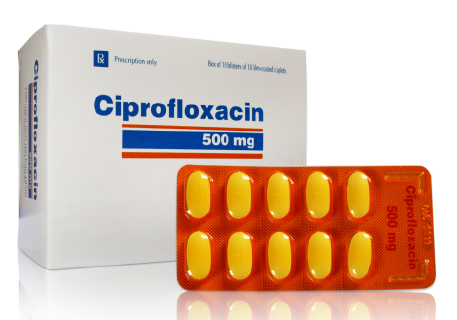
The treatment of acute inflammatory process must be provided urgently, to avoid complications. The most common treatment is performed on an outpatient basis, using conservative means. This requires to solve two main tasks: to improve the supply of blood to the area and eliminate the infection. Etiological treatment includes antibiotics, quinolones group that has proved its effectiveness – Ciprofloxacin is a decent example (you may find the preparation and its analogs at My Canadian Pharmacy as well). It perfectly penetrates into the tissue and kills bacteria. Depending on the severity of the issue, either pills or injections can be used.
With the ineffectiveness of this group of drugs the reserve choice drugs should be used: penicillin or macrolides. The course of treatment is 10-14 days. If the patient has a chronic form of prostatitis, together with antibiotics it is recommended to use beta-blockers. Symptomatic therapy involves the use of anti-inflammatory and pain medications. If the patient suffers from anxiety, it is recommended to take anti-depressants, e.g. Fluoxetine. In case painful urination alpha-1 blockers should be included in treatment. Immunotherapy has a special place in the treatment of prostatitis. The treatment involves normalization of nutrition (excepting too spicy, sugar or salt-rich food), sexual life and mobility.
Possible complications and disease prevention
If a young man doesn’t seek medical help for a long period of time, painful urination can result in stagnation in the bladder. This makes urine ascend into ureters. This facilitates the penetration of infection in the kidney and development of pyelonephritis. The second complication is a significant violation of potency. Prostatitis disrupts sexual function, and if it’s ignored for a long time, complete impotence can develop, with the chances for recovery below average. Ignoring the problem may even result in prostate cancer.
Treating prostatitis is a tough job, preventing it is much easier one. Prevention involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, normalization of sexual relations (sex with a regular partner, use of contraception). Wearing warm clothes and shoes in the cold season is also crucial, as hypothermia is one of the predisposing factors. Prevention includes timely treatment of chronic diseases and daily exercises, or at least plenty of daily movement. By following all these rules the risk of inflammation of the prostate gland is significantly minimized.










