Nitroglycerin (Glyceryl Trinitrate): Nitroglycerin Vs Cardiac Angina, Indication to Use, Pharmacological Effect, Pediatric Use, Side Effects
CONTENT

- Nitroglycerin Vs Cardiac Angina
- Indication to Use
- Nitroglycerin Tablets Composition
- Posology and Method of Administration
- Pharmacological Effect
- Pharmacokinetics
- Nitroglycerin Contraindications
- Nitroglycerin Overdose
- Drug Interaction
- Safety Note
- Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
- Pediatric Use
- Pregnancy and Lactation
- Nitroglycerin Storage Requirements
Nitroglycerin Vs Cardiac Angina
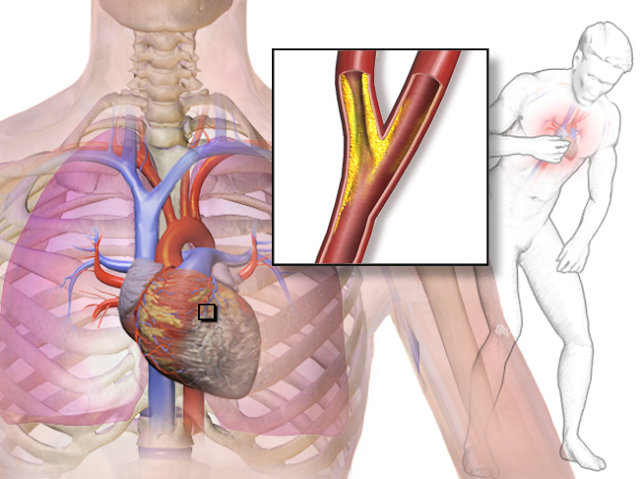 Various diseases of cardio-vascular system became a frequent phenomenon in modern people lives. The causes of this disorder development are abundant. They include sedentary lifestyle, chronic diseases, genetic predisposition, and so on and so forth. Among all the variety of cardio-vascular disorders cardiac angina reminds of itself most often. Cardiac angina attacks are extremely dangerous. Therefore, they should be blocked immediately. In this case tableted Nitroglycerin will come to the rescue. Canadian Pharmacy (mycanadianpharmacyrx.com) is pleased to introduce for your consideration fresh supplies of Nitroglycerin in tableted form at a reasonable price and of high quality. First of all, tableted Nitroglycerin is a medicinal product of synthetic origin which has been known all over the world for hundreds of years.
Various diseases of cardio-vascular system became a frequent phenomenon in modern people lives. The causes of this disorder development are abundant. They include sedentary lifestyle, chronic diseases, genetic predisposition, and so on and so forth. Among all the variety of cardio-vascular disorders cardiac angina reminds of itself most often. Cardiac angina attacks are extremely dangerous. Therefore, they should be blocked immediately. In this case tableted Nitroglycerin will come to the rescue. Canadian Pharmacy (mycanadianpharmacyrx.com) is pleased to introduce for your consideration fresh supplies of Nitroglycerin in tableted form at a reasonable price and of high quality. First of all, tableted Nitroglycerin is a medicinal product of synthetic origin which has been known all over the world for hundreds of years.
Notwithstanding the fact that pharmaceutical market has been constantly replenished by numerous medications of the same action for all these years, Nitroglycerin is still one of the best. It is issued not only in tablets, but also in the form of capsules, solution for injections and spray. It should be mentioned that Nitroglycerin is fast and easily absorbed. A man may start feeling better in a minute after its intake.
Nitroglycerin Indication to Use
- Blockage and prophylactics of cardiac angina attacks.
- Medical rehabilitation after myocardial infarction.
Nitroglycerin Tablets Composition
Active substance: nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate);
Auxiliary agents: lactose monohydrate, povidone 25, cryptocrystalline cryptocrystalline cellulose, cross-carmellose sodium, stearate magnesium.
Posology and Method of Administration
Nitroglycerin is taken by persons above 18 years of age. While prescribing this medication, a doctor should first examine its influence of the level of arterial blood pressure. Nitroglycerin efficiency control should be conducted in accordance with cardiac rhythm and arterial blood pressure level.
Nitroglycerin should be used with first symptoms of cardiac angina attacks. Right after their occurrence, one tablet is required to be put under tongue and keep it in mouth cavity until complete absorption without swallowing it. Traditional dosage of the medication is 1 tablet out under the tongue. In case of absence of antianginal action within 3-5 minutes, 1 tablet of Nitroglycerin may be taken one more time. In case of absence of any therapeutic effect upon using of 2-3 tablets, immediate medical attendance is required.
In case of frequent attack of cardiac angina, it is recommended taking medications of prolonged action.
Pharmacological Effect
Nitroglycerin is a peripheral vasodilator generally impacting venous vessels. Nitroglycerin action is mainly connected with decrease of myocardium demand in oxygen by means of reduction of preload (enlargement of peripheral veins and blood supply decrease to right atrium) and afterload (decrease of overall peripheral vascular resistance).
Nitroglycerin has a slowing down influence on sympathetic tone of vessels inhibiting their vascular component of pain syndrome formation. It causes vasodilation of meningeal vessels which explains the headache after its intake. After the intake of sublingual forms of Nitroglycerin, cardiac angina attack is promptly eliminated in 1,5 minutes. Hemodynamic and antianginal effect preserves from 30 to 60 minutes.
Nitroglycerin enhances the free radical content of nitrogen oxide which activates guanylate cyclase and enhances the amount of cyclic guanosine monophosphate in smooth muscle cells. It vasodilates mainly venous vessels, causes blood storage in venous system and decreases venous reflux of blood to heart (preload) and end-diastolic filling of left ventricle. Systemic arterial vasodilation (generally enlarges large arteries) is accompanied by decrease of peripheral resistance and arterial blood pressure, i.e. afterload.
The decrease of pre- and afterload leads to the reduction of myocardium demand for oxygen; decreases high central venous pressure and pulmonary capillary-wedge pressure; enhances insignificantly cardiac rhythm (reflex tachycardia in response to the decrease of systemic arterial blood pressure and systolic discharge); reduces coronary artery resistance and improves cardiac blood circulation (excluding the cases of excessive drop of arterial blood pressure or significant increase of cardiac rhythm when it is possible to improve coronary blood flow).
Nitroglycerin enlarges huge epicardial sections of coronary arteries, contributes to enhancement of barometric gradient on place of atherosclerotic stenosis of coronary vessel, provides perfusion even in case of near-total stenosis, includes collaterals due to diminishing resistance to blood stream through them.
Pharmacokinetics
Nitroglycerin is fast and completely absorbed from the surface of mucous coat. Sublingual intake causes its fast penetration into systemic circulation. In the dosage of 0,5mg, 100 per cent concentration in blood plasma is achieved in five minutes. The connection with blood protein is 60%.
Nitroglycerin Contraindications
Nitroglycerin is counter-indicative in the following cases:
- Hypersensitivity to nitrates or other components of the drug;
- Genetic galactose intolerance, Lapp-lactase deficit or malabsorption syndrome of glucose-galactose.
- Anemia, increase of intercranial pressure (including cases caused by head injury), cerebral hemorrhage, angle-closure glaucoma, hypotensive condition, hypovolaemia, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, aortal and mitral stenosis, cardiac tamponade, obstructive cardiac decompensation, pericarditis.
- Simultaneous intake with PDE5 inhibitors, such as sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil.
Nitroglycerin Overdose
From the part of cardio-vascular system: vertigo, headache, tachycardia, skin covering hyperaemia. fever sensation, arterial hypotension; seldom (especially in case of overdose) – collapse, cyanosis.
From the part of alimentary system: nausea, vomit.
From the part of central nervous system: seldom (especially in case of overdose) – anxiety, psychotic reactions.
Allergic reactions: seldom – rashes, itching.
Focal reactions: slight itching, burning feeling, redness of skin.
Other: methemoglobinemia.
Treatment: A patient should be placed in the horizontal position. His legs should be lifted. In severe cases, a doctor prescribes plasma expanders, sympathomimetics, or oxygen.
Drug Interaction
 In case of Nitroglycerin co-administration with vasodilators, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, slow channel-blocking agents, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, diuretics, tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, ethanol and ethanol containing drugs, the enhancement of hypotensive effect of glyceryl trinitrate is possible.
In case of Nitroglycerin co-administration with vasodilators, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, slow channel-blocking agents, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, diuretics, tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, ethanol and ethanol containing drugs, the enhancement of hypotensive effect of glyceryl trinitrate is possible.
Simultaneous intake with beta-adrenergic blocking agents and slow channel-blocking agents the antianginal effect gets enhanced.
Co-administration with sympathomimetics may decrease antianginal effect of Nitroglycerin which in its turn may reduce the pressor effect of sympathomimetics (as a result, a patient may experience false arterial hypotension).
Simultaneous intake with remedies with anticholinergic action (including tricyclic antidepressants, disopyramide) may cause hypo salivation and dryness in mouth cavity.
There limited data of the fact that acetylsalicylic acid used in the capacity of pain reliever increases concentration of Nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate) in blood plasma. It may be accompanied by enhancement of hypotensive effect and headaches. A number of research studies have demonstrated the decrease of vasodilating effect of Nitroglycerin on the setting of therapy by means of acetylsalicylic acid. It is considered that the co-administration of Nitroglycerin along with acetylsalicylic acid may cause enhancement of anti-thrombolytic effect of the latter.
In taken combined, Nitroglycerin decreases the impact of acetylcholine, histamine, norepinephrine. Simultaneous intake may increase bioaccessibility of dihydroergotamine and decrease of antianginal effect of Nitroglycerin. Simultaneous intake with procainamide hydrochloride may enhance hypotensive effect and collapse development.
Combined intake with rizatripan and sumatriptan rises the risk of coronary spasm development; with sildenafil – risk of severe arterial hypotension and acute myocardial infarction; with quinidine – orthostatic collapse; with ethanol – sudden weakness and vertigo.
Safety Note
Patients suffering from pronounced cerebral atherosclerosis, disorder of cerebral circulation, severe anemia, or having the underlying risk for postural hypotension, elderly patients and those who suffer from hypovolaemia and pronounced impairments of hepatic and renal functions should take Nitroglycerin carefully.
Long-term intake may lead to tolerability development to nitrates action. In order to prevent from tolerability occurrence, it is recommended observing 10-12hour break in their intake within each 24-hour cycle.
The tablets are recommended for use under tongue if dermal administration of Nitroglycerin causes anginal attack.
During the therapy course a patient must refuse alcohol.
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
Nitroglycerin is characterized by capacity of affecting the reaction rate while driving or using machines. Glyceryl trinitrate may reduce the rate of psychomotor action. Since Nitroglycerin may cause vertigo, patients must make sure that they are not affected by the medicine before fulfilling potentially dangerous activities requiring attention focusing. This effect is aggravated by alcohol.
Pediatric Use
There was no experience of Nitroglycerin application by children. Therefore, its use is not recommended by this age group of patients.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Nitroglycerin intake during pregnancy and lactation period is possible only when potential benefit to the mother outweighs any potential risk to the fetus or baby.
Nitroglycerin Storage Requirements
Do not store above 25°C. This medicine should not be administered upon its expiry period indicated on the package. Expiration period – 2.5 years.